Abstract
Objective
To explore the effect of Compound Tufuling Granules (复方土茯苓颗粒, CTG) on regulating glucose transporter 9 (GLUT9) expression in the kidney to influence the uric acid excretion by the kidney and serum uric acid (SUA) level in hyperuricemia mice.
Methods
Sixty Kunming male mice were randomly divided into the control group, model group, benzbromarone group, and CTG high-, middle- and lowdose groups. The yeast extract and uricase inhibition method were used to build hyperuricemia model, and the corresponding drugs were administrated on the 7th day. On the 21st day the 24-h urine was collected, on the 22nd day the blood was collected, the SUA level was detected by uricase colorimetry, and the mRNA and protein expressions of GLUT9 were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot, respectively.
Results
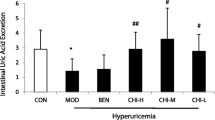
Compared with the model group, the levels of SUA and the mRNA and protein expressions of GLUT9 were signifificantly decreased, and the fraction excretion of uric acid (FEUA) was significantly increased in the CTG groups and benzbromarone group (all P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the above indicators between the CTG high-dose group and benzbromarone group (P>0.05). SUA is positively related to the GLUT9 mRNA and protein expressions in the kidney (P<0.05 or P<0.01).
Conclusions
CTG can signifificantly reduce the SUA and increase the FEUA. In addition, CTG can effectively inhibit the mRNA and protein expressions of GLUT9 in the kidney of hyperuricemia mice to inhibit the uric acid re-absorption, promote uric acid excretion and reduce SUA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang XX, Sun WF, Xu W, Wang T. Assessment on the clinical efficacy and safety of Xiezhuo Chubi Recipe in treating hyperuricemia. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2011;31:1216–1219.
Zhang XX, Sun WF, Xu W, Wang T. Study on influence of Xiezhuo Chubi Decoction on uric acid and URAT1 in hyperuricemia mice. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formul (Chin) 2012;18:144–147.
Sun WF, Zhang XX, Sun FY, Xu W, Liang J, Feng SM, et al. MicroRNA expression patterns of the kidney in hyperuricemia mice treated with Xiezhuo Chubi Decoction. Chin J Integr Med 2011;17:35–42.
Chen GL, Zhang QL, Ma XQ, XU SY. Hyperuricemia model induced by yeast in mice. Chin Pharmacolog Bull (Chin) 2003;19:467–469.
Song LJ, Zhang XY, Xilipu D, Xi QM, Zhao P, Rehemu N. Establishment of a stable hyperuricemia and hyperuricemia renal impairment model in rats. J Xinjiang Med Univ (Chin) 2011;34:55–57.
Liu SF, Zeng XJ. Advance in the research of animal models of hyperuricemia. Basic Clin Med (Chin) 2011;31:344–347.
Pan Z, Duan FJ, Wang YH, Zhang JB, Wei XH. Effect of extract of Cortex Phellodendri and Atractylodes lancea on hyperuricemia in mice. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (Chin) 2008;19:112–113.
Liu XY, Zhu XJ, Guo J, Wu HW, Wang YW. The effect of different strains on mouse hyperucicemia model. Progr Modern Biomed (Chin) 2011;11:4824–4827.
Jin SR, Zheng J, Liu ST. Preliminary studies on animal models of hyperuricemic mice. J Chendu Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 1999;22:49–50.
Sun XL, Wang KY, Zhang DQ. Study on the inflammatory and analgesic effects of Tufuling Injection. Chin J Tradit Med Sci Technol (Chin) 2004;11:231–232.
Xu TT, Cheng ZK, Yin L, Xu WK. Material basis research on the Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae inhibition of xanthine oxidase. J Chin Med Mater (Chin) 2012;35:582–585.
Xia DZ, Zhang Y, Lu GY. Research progress of on flavonoids preventing hyperuricemia and gout. Chin Pharm J (Chin) 2009;44:721–723.
Chen GL, Liu HP, Han R, Xu SY. Studies on the rationality of total saponin of Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae combined with total saponin of Radix Achyranthis Bidentataeon reducing serum uric acid and anti-inflammatory in mice. Chin Pharmacolog Bull (Chin) 2007;23:1467–1471.
Li XL, Li W, Chen GH, Hou SL. Experimental study of Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae on promoting blood circulation. Tradit Chin Med Res (Chin) 1990;3:27–29.
Xu Q, Wang R, Xu LH, Jiang JY. Effect of Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae on cellular immunity and humoral immunity. Chin J Immunol (Chin) 1993;9:39–42.
Chen GL, Lu HX, Wang YY, Li L. Effects and mechanisms of total saponin of Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae and Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae on rat with acute gouty arthritis induced by monosodium urate crystal. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2010;26:34–37.
Wei L, Liu JT, Gou W, Liu CG, Li XK, Wang Z. Experimental study on Fengling Gel in fighting inflammation and analgesia. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2008;42:67–69.
Anzai N, Ichida K, Jutabha P, Kimura T, Babu E, Jin CJ, et al. Plasma urate level is directly regulated by a voltagedriven urate efflux transporter URATv1 (SLC2A9) in humans. J Biol Chem 2008;283:26834–26838.
Dinour D, Gray NK, Campbell S, Shu XH, Sawyer L, Richardson W, et al. Homozygous SLC2A9 mutations cause severe renal hypouricemia. J Am Soc Nephrol 2010;21:64–72.
Caulfield MJ, Munroe PB, O'Neill D, Witkowska K, Charchar FJ, Doblado M, et al. SLC2A9 is a high-capacity urate transporter in humans. PLoS Med 2008;5:1509–1523.
Kimura T, Amonpatumrat S, Tsukada A, Fukutomi T, Jutabha P, Thammapratip T, et al. Increased expression of SLC2A9 decreases urate excretion from the kidney. Nucleos Nucleot Nucleic Acids 2011;30:1295–1301.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Yw., Sun, Wf., Zhang, Xx. et al. Compound Tufuling Granules (复方土茯苓颗粒) regulate glucose transporter 9 expression in kidney to influence serum uric acid level in hyperuricemia mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 21, 823–829 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2052-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2052-2