Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of Yishen Jiangzhuo Granules (益肾降浊冲剂, YSJZG) on mitochondrial injury and regeneration and renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis in chronic renal failure (CRF) rats and explore its mechanism from molecular pathology, gene, protein levels, and relative pathway.
Methods
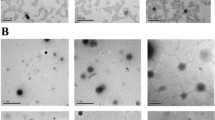
The CRF rat model was established using 5/6 nephrectomy. Sixty rats were randomly divided into six groups: sham-operation group, model (CRF) group, Niaoduqing Granules (尿毒清颗粒)-treated group [5 g/(kg.day)], low-, moderate-, and high-dose [L-YSJZG, M-YSJZG, H-YSJZG at 3, 6, and 9 g/(kg day)] YSJZG-treated group (n=10 each). The levels of serum creatinine (Scr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and 24-h urine protein were assessed after 10 weeks of treatment. The tubulointerstitial injury and collagen deposition were evaluated using periodic acid-schiff stain and Masson staining. Renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis was assessed using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling assay, mitochondrial injury was observed using an electron microscope, and superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were assessed using chromometry. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) expression was assessed using immunohistochemistry. The expressions of Bax, Bcl-2, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator- 1α (PGC-1α), mitochondrial transcription factor A (Tfam), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) phosphorylation were evaluated by Western blot.
Results
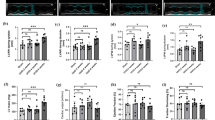
YSJZG decreased the 24-h urine protein, BUN, Scr, remnant kidney weight-to-body weight ratio, renal tubular injury, deposition of collagen, and the apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells in a dose-dependent manner. YSJZG dose-dependently restored the number and structure of mitochondria and the expression of Tfam and PCG-1α, up-regulated the expression of Bcl-2, and inhibited the expression of Bax. YSJZG also dose-dependently inhibited TGF-β1 expression, increased SOD and GSH activity, decreased the MDA level, and inhibited p38MAPK and pERK1/2 phosphorylation (all P<0.01).
Conclusion
YSJZG improved the renal function in rats with CRF and inhibited the progression of tubulointerstitial fibrosis by dose-dependently alleviating mitochondrial injury, restoring the expression of Tfam and PCG-1α, and inhibiting renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis through inhibiting activation of reactive oxygen species-MAPK signaling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma K, Cook A, Smith M, Valancius C, Inscho EW. TGF-β impairs renal autoregulation via generation of ROS. Am J Physiol Renal 2005;288: F1069–F1077.
Sun L, Xiao L, Nie J, Liu FY, Ling GH, Zhu XJ, et al. p66Shc mediates high-glucose and angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress renal tubular injury via mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic pathway. Am J Physiol Renal 2010;299: F1014–F1025.
Funk JA, Odejinmi S, Schnellmann RG. SRT1720 induces mitochondrial biogenesis and rescues mitochondrial function after oxidant injury in renal proximal tubule cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2010;333:593–601.
Martin MM, Buckenberger JA, Jiang J, Malana GE, Knoell DL, Feldman DS, et al. TGF-β1 stimulates human AT1 receptor expression in lung fibroblasts by cross talk between the Smad, p38 MAPK, JNK, and PI3K signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Lung-C 2007;293:L790–L799.
Ventura-Clapier R, Garnier A, Veksler V. Transcriptional control of mitochondrial biogenesis: the central role of PGC-1a. Cardiovasc Res 2008;79:208–217.
Xu YF, Ruan SW, Zhang Z. Protective effect and mechanism of Yishenjiangzhuo Granules on renal glomerulosclerosis. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm (Chin) 2011;26:2844–2848.
Kim K J, Moradi H, Yuan J, Norris K, Vaziri ND. Renal mass reduction results in accumulation of lipids and dysregulation of lipid regulatory proteins in the remnant kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2009;296:F1297–F1306.
Xu YF, Ruan SW, Wan JX, Zhang Z. Effect of Yishenjiangzhuo Granules on accumulation of lipids and tubulointerstitial injury in remnant kidney of 5/6 nephrectomy rats. Chin J Integr Trad West Nephrol (Chin) 2011;12:852–855.
Xu Y, Ruan S, Xie H, Lin JM. Role of LOX-1 in Ang II-induced oxidative functional damage in renal tubular epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med 2010;26: 679–690.
Zeisberg M, Hanai J, Sugimoto H, Mammoto T, Charytan D, Strutz F, et al. BMP-7 counteracts TGF-beta1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition and reverses chronic renal injury. Nat Med 2003;9:964–968.
Rouschop KMA, Claessen N, Pals ST, Weening JJ, Florquin S. CD44 disruption prevents degeneration of the capillary network in obstructive nephropathy via reduction of TGF-β1-induced apoptosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;17:746–753.
Doughan AK, Harrison DG, Dikalov SI. Molecular mechanisms of angiotensin II-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction linking mitochondrial oxidative damage and vascular endothelial dysfunction. Circ Res 2008; 102:488–496.
Rego AC, Oliveira CR. Mitochondrial dysfunction and reactive oxygen species in excitotoxicity and apoptosis: implications for the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem Res 2003;28:1563–1574.
Rasbach KA, Schnellmann RG. Signaling of mitochondrial biogenesis following oxidant injury. J Biol Chem 2007;282:2355–2362.
Park CB, Larsson NG. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in disease and aging. J Cell Biol 2011;193:809–818.
Arany Z, He H, Lin J, Hoyer K, Handschin C, Toka O, et al. Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1 alpha controls the energy state and contractile function of cardiac muscle. Cell Metab 2005;1:259–271.
Adhihetty PJ, Taivassalo T, Haller RG, Walkinshaw DR, Hood DA. The effect of training on the expression of mitochondrial biogenesis-and apoptosis-related proteins in skeletal muscle of patients with mtDNA defects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007;293:E672–E680.
Ryan MT, Hoogenraad NJ. Mitochondrial-nuclear communications. Annu Rev Biochem 2007;76:701–722.
Arany I, Megyesi JK, Kaneto H, Tanaka S, Safirstein RL. Activation of ERK or inhibition of JNK ameliorates H(2)O(2) cytotoxicity in mouse renal proximal tubule cells. Kidney Int 2004;65:1231–1239.
Adhihetty PJ, Uguccioni G, Leick L, Hidalgo J, Pilegaard H, Hood DA. The role of PGC-1α on mitochondrial function and apoptotic susceptibility in muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2009;297:C217–C225.
Valle I, Alvarez-Barriento A, Arza E, Lamas ST, Monsalve M. PGC-1α regulates the mitochondrial antioxidant defense system in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 2005;66:562–573.
Hu C, Dandapat A, Sun L, Khan JA, Liu Y, Hermonat PL, et al. Regulation of TGFbeta1-mediated collagen formation by LOX-1: studies based on forced overexpression of TGFbeta1 in wild-type and lox-1 knock-out mouse cardiac fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 2008;283:10226–10231.
Rhyu DY, Yang Y, Ha H, Lee GT, Song JS, Uh ST, et al. Role of reactive oxygen species in TGF-beta1-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and epithelialmesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005;16:667–675.
Lee EA, Seo JY, Jiang Z, Yu MR, Kwon MK, Ha H, et al. Reactive oxygen species mediate high glucose-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 up-regulation in mesangial cells and in diabetic kidney. Kidney Int 2005;67:1762–1771.
Xu YF, Yang SY, Huang JY, Ruan SW, Zhang Z, Lin JM. TGF-β1 induced autophagy and promoted apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med 2012;29:781–790.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Yf., Ruan, Sw., Lin, Jm. et al. Yishen Jiangzhuo Granules (益肾降浊冲剂) affect tubulointerstitial fibrosis via a mitochondrion-mediated apoptotic pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 21, 928–937 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2078-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2078-5