Abstract
Objective
To explore the neuroprotective effects of electroacupuncture (EA) on hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and to further investigate the role of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family receptor member RET (rearranged during transfection) and its key downstream phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI-3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway in the process.
Methods
A total of 220 seven-day-old SD rats (of either sex, from 22 broods) were randomly divided into two groups, one (30 rats) for sham-surgery group and the other (190 rats) for HIE model group. The HIE model was established using the left common carotid artery ligation method in combination with hypoxic treatment. The successfully established rats were randomly divided into five groups, including control model group, EA group, sham-EA group, antagonist group and antagonist plus electroacupuncture group, with 35 rats in each group. Baihui (GV 20), Dazhui (GV 14), Quchi (LI 11) and Yongquan (KI 1) acupoints were chosen for acupuncture. EA was performed at Baihui and Quchi for 10 min once a day for continuous 1, 3, 7 and 21 days, respectively. The rats were then killed after the operation and injured cerebral cortex was taken for the measurement of neurologic damage by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and the degenerative changes of cortical ultrastructure by transmission electron microscopy. RET mRNA level and Akt protein level were detected by real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blot analysis, respectively.
Results
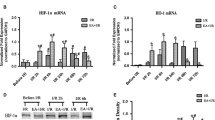
EA could ameliorate neurologic damage of the first somatic sensory area (S1Tr) and alleviate the degenerative changes of ultrastructure of cortical neurons in rats subjected to HIE. And the longer acupuncture treatment lasted, the better its therapeutic effect would be. This was accompanied by gradually increased expression of GDNF family receptor RET at the mRNA level and its downstream signaling Akt at the protein level in the ischemic cortex.
Conclusion
EA has neuroprotective effects on HIE and could be a potential therapeutic strategy for HIE in the neonate. Activation of RET/Akt signaling pathway might be involved in this process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shankaran S. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and novel strategies for neuroprotection. Clin Perinatol 2012;39:919–929.
Parker L, Kenner C. Neuroprotective strategies for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Newborn Infant Nurs Rev 2012;12:8–11.
Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, Tarnow-Mordi WO, Inder TE, Davis PG. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;1:CD003311.
Manni L, Albanesi M, Guaragna M, Barbaro Paparo S, Aloe L. Neurotrophins and acupuncture. Auton Neurosci 2010;157:9–17.
Joh TH, Park HJ, Kim SN, Lee H. Recent development of acupuncture on Parkinson's disease. Neurol Res 2010;32 Suppl 1:5–9.
Li M, Peng J, Song Y, Liang H, Mei Y, Fang Y. Electroacupuncture combined with transcranial magnetic stimulation improves learning and memory function of rats with cerebral infarction by inhibiting neuron cell apoptosis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci (Chin) 2012;32:746–749.
Gao J, Wang S, Wang X, Zhu C. Electroacupuncture enhances cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation in young rat brains. Neurol Sci 2011;32:369–374.
Wang TT, Yuan Y, Kang Y, Yuan WL, Zhang HT, Wu LY, et al. Effects of acupuncture on the expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2/bFGF) in the left sixth lumbar dorsal root ganglion following removal of adjacent dorsal root ganglia. Neurosci Lett 2005;382:236–241.
Liang XB, Luo Y, Liu XY, Lu J, Li FQ, Wang Q, et al. Electroacupuncture improves behavior and upregulates GDNF mRNA in MFB transected rats. Neuroreport 2003;14:1177–1181.
Hoke A, Cheng C, Zochodne DW. Expression of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family of growth factors in peripheral nerve injury in rats. Neuroreport 2000;11:1651–1654.
Ikeda T, Koo H, Xia YX, Ikenoue T, Choi BH. Bimodal upregulation of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in the neonatal rat brain following ischemic/hypoxic injury. Int J Dev Neurosci 2002;20:555–562.
Ikeda T, Xia XY, Xia YX, Ikenoue T, Han B, Choi BH. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor protects against ischemia/hypoxia-induced brain injury in neonatal rat. Acta Neuropathol 2000;100:161–167.
Katsuragi S, Ikeda T, Ikenoue T. A strategy to treat neonatal hypoxic encephalopathy using glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. No To Hattatsu 2011;43:265–272.
Wang X, Guo S, Lu S, Zhou J, Li J, Xia S. Ultrasoundinduced release of GDNF from lipid coated microbubbles injected into striatum reduces hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rats. Brain Res Bull 2012;88:495–500.
Baloh RH, Enomoto H, Johnson EM, Jr., Milbrandt J. The GDNF family ligands and receptors-implications for neural development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2000;10:103–110.
Wang HQ, Xu YX, Zhu CQ. Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 by acteoside through ERK and PI3 K/Akt pathway confer neuroprotection against beta-amyloidinduced neurotoxicity. Neurotox Res 2012;21:368–378.
Wang HJ, Cao JP, Yu JK, Gao DS. Role of PI3-K/Akt pathway and its effect on glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in midbrain dopamine cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007;28:166–172.
Rice JE, 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 1981;9:131–141.
Zheng GQ. Methodological standards for experimental research on stroke using scalp acupuncture. Acupunct Electrother Res 2009;34:1–13.
Longo UG, Franceschi F, Ruzzini L, Rabitti C, Morini S, Maffulli N, et al. Characteristics at haematoxylin and eosin staining of ruptures of the long head of the biceps tendon. Br J Sports Med 2009;43:603–607.
Fang Z, Ning J, Xiong C, Shulin Y. Effects of Electroacupuncture at head points on the function of cerebral motor areas in stroke patients: a PET study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012;2012:902413.
Kim M, Chung Y, Jung H, Park M, Han Y. Scalp electroacupuncture at the Baihui acupoint (DU 20) improves functional recovery in rats with cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res 2011;6:2822–2828.
Chuang C, Hsieh C, Li T, Lin J. Acupuncture stimulation at Baihui acupoint reduced cerebral infarct and increased dopamine levels in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and ischemia-reperfusion injured Sprague-Dawley rats. Am J Chin Med 2007;35:779–791.
Liu H, Shen X, Tang H, Li J, Xiang T, Yu W. Using microPET imaging in quantitative verification of the acupuncture effect in ischemia stroke treatment. Sci Rep 2013;3:1070.
Hong J, Wu G, Zou Y, Tao J, Chen L. Electroacupuncture promotes neurological functional recovery via the retinoic acid signaling pathway in rats following cerebral ischemiareperfusion injury. Int J Mol Med 2013;31:225–231.
Chen A, Lin Z, Lan L, Xie G, Huang J, Lin J, et al. Electroacupuncture at the Quchi and Zusanli acupoints exerts neuroprotective role in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med 2012;30:791–796.
Xue WG, Ge GL, Zhang Z, Xu H, Bai LM. Effect of electroacupuncture on the behavior and hippocampal ultrastructure in APP 695 V 717 I transgenic mice. Acupunct Res (Chin) 2009;34:309–314.
Xue WG, Zhang Z, Xu H, Wu HX, Bai LM. Effect of electroacupuncture on learning-memory ability, and Abeta and LRP1 immunoactivity in hippocampal sulcus microvessels in APP transgenic mice. Acupunct Res (Chin) 2011;36:95–100.
Ji XQ, Zhang ZL. Observation on therapeutic effect of nuchal acupuncture and abdominal acupuncture for treatment of stroke patients with spastic hemiplegia. Acupunct Res (Chin) 2009;29:961–965.
Zhou W, Liu H, Wang LP, Xu ZG, Feng YW, Lu H, et al. Effect of alternative administration of scalp-acupuncture, body-acupuncture and abdominal-acupuncture on the upper-limb dyscinesia in patients with stroke. Acupunct Res (Chin) 2009;34:128–131.
Wong V, Cheuk D, Chu V. Acupuncture for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;1:CD007968.
Liu Y, Zou LP, Du JB, Wong V. Electroacupuncture protects against hypoxic-ischemic brain-damaged immature rat via hydrogen sulfide as a possible mediator. Neurosci Letters 2010;485:74–78.
Ding CH, Liu HR, Zhang SD, Ling YL. Treatment of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy of newly born rats by acupuncture. Chin J Applied Physiol (Chin) 2005;21:200–201.
Aoi M, Date I, Tomita S, Ohmoto T. Single administration of GDNF into the striatum induced protection and repair of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system in the intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine injection model of hemiparkinsonism. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2001;17:31–38.
Garces A, Haase G, Airaksinen MS, Livet J, Filippi P, deLapeyriere O. GFR alpha 1 is required for development of distinct subpopulations of motoneuron. J Neurosci 2000;20:4992–5000.
Oppenheim RW, Houenou LJ, Parsadanian AS, Prevette D, Snider WD, Shen L. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and developing mammalian motoneurons: regulation of programmed cell death among motoneuron subtypes. J Neurosci 2000;20:5001–5011.
Nakajima T, Iwabuchi S, Miyazaki H, Okuma Y, Kuwabara M, Nomura Y, et al. Preconditioning prevents ischemiainduced neuronal death through persistent Akt activation in the penumbra region of the rat brain. J Vet Med Sci 2004;66:521–527.
Ohba N, Kiryu-Seo S, Maeda M, Muraoka M, Ishii M, Kiyama H. Transgenic mouse overexpressing the Akt reduced the volume of infarct area after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurosci Lett 2004;359:159–162.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the 45th China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 20090450856)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, T., Xu, Ng., Yang, Zh. et al. Neuroprotective effects of electroacupuncture on hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in newborn rats are associated with increased expression of GDNF-RET and protein kinase B. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 22, 457–466 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-1972-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-1972-1