Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effect and safety of acupuncture therapy on patients with moderate to severe allergic rhinitis.
Methods
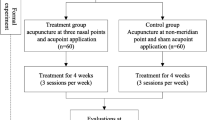
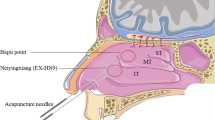
A non-randomized controlled design was used to compare between the acupuncture group and the medication group. The acupuncture group received 8-week acupuncture therapy, and the medication group received budesonide nasal spray with cetirizine tablets for 8 weeks. The clinical symptoms and signs were analyzed before treatment, at 4 and 8 weeks after the start of treatment, and at 12 weeks after the end of treatment. Furthermore, the clinical efficacy and safety indicators were compared between the two groups.
Results
A total of 76 participants consisting of 38 in each of the two groups were enrolled. The scores of each clinical symptom and sign, including sneezing, runny nose, stuffy nose, nasal itching, and turbinate edema, and the total scores decreased over time in both groups (all P<0.05); and no difference was found in the scores between the two groups (P>0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the effective rates of the acupuncture group at 4 and 8 weeks after the start of treatment as well as at 12-week follow-up compared with those of the medication group (83.3% vs. 91.2%, and 94.4 % vs. 85.3%; and 80.6 % vs. 82.4%, all P>0.05). Experimental items including blood routine, urine routine, aspartate transaminase, alanine aminotransferase, urea nitrogen and creatinine were all in the normal reference ranges during the treatment in the acupuncture group.
Conclusions
Acupuncture therapy has a comparable effect to the medication treatment on patients with moderate to severe allergic rhinitis, and it is safe with no severe adverse effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousquet J, Van CP, Khaltaev N, Aria Workshop Group, World Health Organization Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001;108:S147–S33.
Han DM, Zhang L, Huang D, Wu YF, Dong Z, Xu G, et al. Self-reported prevalence of allergic rhinitis in 11 cities of China. Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck (Chin) 2007;42:378–384.
Marple BF, Fornadley JA, Patel AA, Fineman SM, Fromer L, Krouse JH, et al. Keys to successful management of patients with allergic rhinitis: focus on patient confidence, compliance, and satisfaction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2007;136:107–124.
Ridolo E, Montagni M, Melli V, Braido F, Incorvaia C, Canonica GW. Pharmacotherapy of allergic rhinitis: current options and future perspectives. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2014;15:73–83.
Braido F, Sclifò F, Ferrando M, Canonica GW. New therapies for allergic rhinitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2014;14(422):1–8.
Xue CC, English R, Zhang JJ, Da Costa C, Li CG. Effect of acupuncture in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Chin Med 2002;30:1–11.
Xue CC, An XD, Cheung TP, Costa CD, Lenon GB, Thien FC, et al. Acupuncture for persistent allergic rhinitis: a randomized, sham-controlled trial. Med J Aust 2007;187:337–341.
Shi ZH, Wang P, Chen S, Fu Y, Wang P, Wang YM, et al. Randomized controlled clinical study on treatment of allergic rhinitis with needling therapy of regulating mind. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med (Clin Med, Chin) 2013;20(2):47–49.
Brinkhaus B, Ortiz M, Witt CM, Roll S, Linde K, Pfab F, et al. Acupuncture in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2013;158:225–234.
Roberts J, Huissoon A, Dretzke J, Wang D, Hyde C. A systematic review of clinical effectiveness of acupuncture for allergic rhinitis. BMC Complement Altern Med 2008;8(13):1–10.
Lee MS, Pittler MH, Shin BC, Kim JI, Ernst E. Acupuncture for allergic rhinitis: a systematic review. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2009;102:269–279.
Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Casale TB, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;126:466–476.
Magnusson AL, Svensson RE, Leirvik C, Gunnarsson RK. The effect of acupuncture on allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Chin Med 2004;32:105–115.
Editorial Board of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Otolaryngology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Allergic rhinitis diagnosis and treatment guidelines (2009, Wuyishan). Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg (Chin) 2009;44:977–978.
Editorial Board of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Otorhinolaryngology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Principles and recommendations on diagnosis and treatment of allergic rhinitis (2004, Lanzhou). Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck (Chin) 2005;40:166–167.
Choi SM, Park JE, Li SS, Jung H, Zi M, Kim TH, et al. A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial testing the effects of acupuncture on allergic rhinitis. Allergy 2013;68:365–374.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Key Project of Zhejiang Province Pharmaceutical Administration, China (No. 2010ZZ001) and Key Disciplines in Integrative Medicine of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2012-XK-A04)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yd., Jin, Xq., Yu, Mh. et al. Acupuncture for moderate to severe allergic rhinitis: A non-randomized controlled trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 22, 518–524 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2453-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2453-x