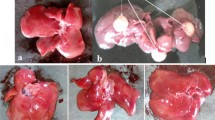
Abstract
Objective
To study whether the ethanol extract of Phellinus merrillii (EPM) has chemopreventive potential against liver carcinogenesis.
Methods
Thirty male Spraque-Dawley rats were randomly divided into control group, EPM control group, hepatocarcinoma control group, low-dose EPM group and high-dose EPM group, 6 in each group. Using the Solt and Farber protocol in a rat model of hepatocarcinogenesis, the chemopreventive effect of EPM on diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-initiated, 2-acetylaminofluorene (2-AAF) and partial hepatectomy (PH)-promoted liver carcinogenesis in rats was evaluated. Basic pathophysiological and histological examinations, together with the serum levels of glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (sGOT), glutamic pyruvic transaminase (sGPT) and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GT) were measured.
Results
Treatment of EPM at the concentration of 2 g/kg body weight in the diet for 8 weeks clearly prevented the development of carcinogenesis and reduced the levels of sGOT, sGPT, and serum γ-GT of rats as compared with the hepatocarcinoma control group (P<0.05 or P<0.01). These phenotypes were accompanied by a significant increase in natural killer cell activity.
Conclusion
EPM showed a strong liver preventive effect against DEN+2-AAF+PH-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in a rat model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zjawiony JK. Biologically active compounds from phyllophorales (Polypore) Fungi. J Nat Prod 2004;67:300–310.
Zhong XH, Ren K, Lu SJ, Yang SY, Sun DZ. Progress of research on Inonotus obliquus. Chin J Integr Med 2009;15:156–160.
Xiao GL, Zhang CH, Liu FY, Chen ZH, Hu SY. Clinical experience in treatment of Amanita mushroom poisoning with Glossy Ganoderma Decoction and routine Western medicines. Chin J Integr Med 2007;13:145–147.
Takeda K, Okumura K. CAM and NK cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2004;1:17–27.
Park YM, Won JH, Kim YH, Choi JW, Park HJ, Lee KT. In vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of the methanol extract of Inonotus obliquus. J Ethnopharmacol 2005;101:120–128.
Nakamura T, Matsugo S, Uzuka Y, Matsuo S, Kawagishi H. Fractionation and anti-tumor activity of the mycelia of liquid-cultured Phellinus linteus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2004;68:868–872.
Hwang HJ, Kim SW, Lim JM, Joo JH, Kim HO, Kim HM, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of crude exopolysaccharides produced by a medicinal mushroom Phellinus baumii in streptozotocininduced diabetic rats. Life Sci 2005;76:3069–3080.
Xiao PG. Some hot spots in the study of Chinese drugs in the 21st Century. Chin J Integr Med 2004;10:82–85.
Jeon TI, Hwang SG, Lim BO, Park DK. Extracts of Phellinus linteus grown on germinated brown rice suppress liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Biotechnol Lett 2003;25:2093–2096.
Lin SB, Li CH, Lee SS, Kan LS. Triterpene-enriched extracts from Ganoderma lucidum inhibit growth of hepatoma cells via suppressing protein kinase C, activating mitogen-activated protein kinases and G2-phase cell cycle arrest. Life Sci 2003;72:2381–2390.
Shon YH, Nam KS. Antimutagenicity and induction of anticarcinogenic phase II enzymes by basidiomycetes. J Ethnopharmacol 2001;77:103–109.
Kim SH, Lee HS, Lee S, Cho J, Ze K, Sung J, et al. Mycelial culture of Phellinus linteus protects primary cultured rat hepatocytes against hepatotoxins. J Ethnopharmacol 2004;95:367–372.
Matsuba S, Matsuno H, Sakuma M, Komatsu Y. Phellinus linteus extract augments the immune response in mitomycin C-induced immunodeficient mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2008;5:85–90.
Kim SH, Song YS, Kim SK, Kim BC, Lim CJ, Park EH. Anti-inflammatory and related pharmacological activities of the n-BuOH subfraction of mushroom Phellinus linteus. J Ethnopharmacol 2004;93:141–146.
Chang HY, Peng WH, Sheu MJ, Huang GJ, Tseng MC, Lai MT, et al. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of ethanol extract from Phellinus merrillii on carbon tetrachloride induced liver damage. Am J Chin Med 2007;35:793–804.
Chang HY, Ho YL, Sheu MJ, Lin YH, Tseng MC, Wu SH, et al. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of Phellinus merrillii extracts. Bot Stud 2007;48:407–417.
Solt D, Farber E. New principle for the analysis of chemical carcinogenesis. Nature 1976;263:701–703.
Yao DF, Huang ZW, Chen SZ, Huang JF, Lu JX, Xiao MB, et al. Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma by quantitative detection of hepatoma-specific bands of serum gammaglutamyltransferase. Am J Clin Pathol 1998;110:743–749.
Kojima K, Ogihara Y, Sakai Y, Mizukami H, Nagatsu A. HPLC profiling of Phellinus linteus. J Nat Med 2008;62:441–446.
Höppner M, Luhm J, Schlenke P, Koritke P, Frohn C. A flow-cytometry based cytotoxicity assay using stained effector cells in combination with native target cells. J Immunol Methods 2002;267:157–163.
Sehrawat A, Sultana S. Evaluation of possible mechanisms of protective role of Tamarix gallica against DEN initiated and 2-AAF promoted hepatocarcinogenesis in male Wistar rats. Life Sci 2006;79:1456–1465.
Chung KS, Lee WC, Sung JM. The antioxidant effect of the basidiocarps of Phellinus spp. J Agric Sci 1998;40:51–56.
Jeena KJ, Joy KL, Kuttan R. Effect of Emblica officinalis, Phyllanthus amarus and Picrorrhiza kurroa on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 1999;136:11–16.
Singh JP, Selvendiran K, Banu SM, Padmavathi R, Sakthisekaran D. Protective role of apigenin on the status of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense against hepatocarcinogenesis in Wistar albino rats. Phytomedicine 2004;11:309–314.
Chenoweth MB, Hake CL. The smaller halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbons. Annu Rev Pharmacol 1962;2:363–398.
Wu W, Yao DF, Yuan YM, Fan JW, Lu XF, Li XH, et al. Combined serum hepatoma-specific alpha-fetoprotein and circulating alpha-fetoprotein-mRNA in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2006;5:538–544.
Xu K, Meng XY, Wu JW, Shen B, Shi YC, Wei Q. Diagnostic value of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase isoenzyme for hepatocellular carcinoma: a 10-year study. Am J Gastroenterol 1992;87:991–995.
Wu JW, Meng XY, Xu KC, Wei Q, Shi YZ, Yi L. Simultaneous determination of multiple markers of primary liver cancer: diagnostic significance. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1988;13:29–35.
Bellini M, Tumino E, Giordani R, Fabrini G, Costa F, Galli R, et al. Serum γ-glutamyl transferase isoforms in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol 1997;32:259–266.
Yao DF, Dong ZZ, Yao DB, Wu XH, Wu W, Qiu LW, et al. Abnormal expression of hepatoma-derived gammaglutamyltransferase subtyping and its early alteration for carcinogenesis of hepatocytes. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2004;3:564–570.
Tang ZY. Fighting against cancer by integrative medicine. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:323–324.
Schattner A, Duggan DB. Natural killer cells toward clinical application. Am J Hematol 1985;18:435–443.
Kim GY, Lee JY, Lee JO, Ryu CH, Choi BT, Jeong YK, et al. Partial characterization and immunostimulatory effect of a novel polysaccharide-protein complex extracted from Phellinus linteus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2006;70:1218–1226.
Bodeker G. Integrative oncology meets immunotherapy: new prospects for combination therapy grounded in Eastern medical knowledge. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:652–662.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. DAI Yu-cheng, Institute of Applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Science and Dr. WU Sheng-hua, Department of Botany, National Museum of Natural Science for identifying the material to be PM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by China Medical University Tsuzuki Institute for Traditional Medicine (No. CMU95-PH-11 and No. CMU97-232), the National Science Council (No. NSC 95-2320-B-182-059-MY3) and Chang Gung University (No. CMRPD160271), Taiwan, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Ch., Chang, Hy., Chen, Yc. et al. Ethanol extract of Phellinus merrillii protects against diethylnitrosamine- and 2-acetylaminofluorene-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 23, 117–124 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2513-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-016-2513-2